Have you ever wondered how some brands effortlessly capture your attention, earn your trust, and make you eager to engage with them?
It’s not just a stroke of luck; it’s the magic of content marketing.
Content marketing forms real bonds in a world full of info and entertainment.
It’s all about crafting engaging stories, sharing useful insights, and sparking meaningful conversations.
But what exactly is content marketing, and how does it work?
Let’s explore.
We’ll look at the four key components of content marketing, its types, and many more, each with its role in the marketing world.
Let’s dive straight into it.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Content Marketing?

Content marketing is a strategic approach where businesses use valuable and relevant content to connect with their target audience.
Instead of directly advertising products or services, content marketing aims to provide information, solve problems, and build trust.
Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Valuable Content: Content marketing involves creating content people find useful, interesting, or entertaining. It can be in various forms like blog articles, videos, social media posts, infographics, or podcasts.
- Audience Focus: The main focus is on understanding the needs and interests of your audience. You create content that addresses their questions, concerns, or interests.
- Building Trust: Instead of pushing products, content marketing builds trust by offering valuable information. People who see your brand as a helpful resource will likely engage and eventually become customers.
- Relationship Building: Content marketing is like having a conversation with your audience. You share knowledge, entertain, or provide solutions, which helps form a connection.
- Long-Term Strategy: It’s not about quick sales but creating lasting relationships. Content marketing requires consistency and patience to see results.
- Measurable Results: You can measure the impact of content marketing through metrics like website traffic, engagement, leads generated, and customer conversions.
In simple terms, content marketing is about creating content that people love, using it to connect with them, and gradually turning them into loyal customers.
It’s a customer-centric and trust-building approach that helps businesses grow over time.
Content Marketing Trends and Statistics to Know
Are you curious about how many businesses use content marketing and what it means for their success?
Here’s the lowdown:
- In a Semrush survey, 91% of marketing professionals found success with content marketing in 2021.
- In 2022, Gen Z gave the thumbs up to Instagram as their favorite social media app.
- According to the Content Marketing Institute, 73% of B2B and 70% of B2C marketers include content marketing in their plans.
- And here’s a cost-saving tip for marketers: 44% say teaming up with smaller influencers is a wallet-friendly choice.
- But not everyone has a clear strategy. The B2B Content Marketing Study by CMI showed that 40% of B2B marketers have a documented content marketing plan, 33% have a plan but haven’t written it down, and 27% have no plan.
- When it comes to trusting product recommendations, a whopping 50% of Millennials put their faith in influencers.
Here’s an interesting twist: About half of all marketers choose to get help by outsourcing parts of their content marketing.
Lastly, due to the pandemic, content usage shot up by 207%.
Exciting times for content marketing, right?
The Four Main Components of Content Marketing

Content marketing thrives on a strategic blend of four primary content types, each serving a distinct purpose in engaging and converting your audience.
Let’s explore these core components clearly and concisely:
1. Awareness Content
Purpose:
Awareness content aims to introduce your brand to a wider audience and create initial interest.
It’s about building brand recognition and visibility.
Examples:
Blog posts, social media updates, infographics, and videos that highlight industry trends, shareable facts, and general information related to your field.
For instance, a tech company might create a blog post about “The Evolution of Smartphones” to pique the interest of potential customers interested in tech gadgets.
2. Thought Leadership Content
Purpose:
Thought leadership content positions your brand as an industry authority. It showcases your expertise, knowledge, and innovative thinking.
Examples:
In-depth articles, whitepapers, webinars, and podcasts that delve into complex industry topics share research findings or offer unique insights.
Imagine a marketing agency publishing a comprehensive whitepaper on “The Future of Digital Marketing,” establishing itself as a trusted resource for marketing trends.
3. Consideration Content
Purpose:
Consideration content helps your audience evaluate your products or services.
It provides valuable information to assist potential customers in making informed decisions.
Examples:
Product comparison guides, case studies, customer testimonials, and interactive tools that showcase how your offerings solve specific problems.
For instance, an e-commerce platform might create a product comparison guide highlighting the features and benefits of different smartphones to assist shoppers in purchasing decisions.
4. Sales Content
Purpose:
Sales content is designed to convert prospects into paying customers.
It’s focused on driving action, such as purchasing, signing up for a service, or requesting a demo.
Examples:
Product descriptions, pricing pages, email campaigns, and call-to-action (CTA) elements guide visitors toward the desired action.
Consider an online subscription service using a compelling email campaign to encourage users to sign up for a free trial of their software.
These four core components work in harmony to guide your audience through the customer journey, from initial awareness to becoming loyal customers.
An effective content marketing strategy carefully balances and leverages each type of content to achieve overarching marketing objectives.
What are the Core Principles of Content Marketing?
Content marketing operates on several fundamental principles, which serve as guiding pillars for creating and implementing effective strategies.
These principles are essential for crafting content that resonates with your audience and drives meaningful engagement.
Let’s explore these core principles in simple terms:
1. Audience-Centric Approach
Content marketing revolves around your target audience.
Understand their needs, preferences, pain points, and interests.
Create content that addresses their specific concerns and provides value.
Example:
If you run a pet store, your audience-centric content would include articles on pet care, training tips, and product reviews based on what pet owners seek.
2. Valuable and Relevant Content
Content should offer valuable information, insights, or solutions.
It should be relevant to your audience’s interests and concerns.
Avoid overly promotional or sales-focused content.
Example:
A nutritionist could create valuable content by sharing healthy recipes, dietary tips, and nutritional facts, helping their audience make informed choices.
3. Consistency
Consistency is a key.
Regularly publish content to maintain engagement and build trust.
Set a content schedule that your audience can rely on.
Example:
A fashion blog consistently releases new outfit ideas, style guides, and trend updates to keep its readers engaged.
4. Authenticity and Transparency
Authenticity matters.
Be transparent about your brand, products, and values.
Avoid deceptive or misleading content.
Building trust is a long-term investment.
Example:
An eco-friendly brand should transparently communicate its sustainability practices, including the sourcing and production of eco-conscious products.
5. Storytelling
Stories resonate with people. Use storytelling to convey your brand’s mission, values, and the impact of your products or services.
Example:
A nonprofit organization can share success stories of individuals or communities positively affected by their initiatives, making their cause more relatable.
6. Multi-Platform Presence
Reach your audience where they spend their time.
To extend your content’s reach, utilize various platforms like websites, social media, email, and more.
Example:
A travel agency shares travel guides on its website stunning destination photos on Instagram, and engages with travelers through a newsletter.
7. Measure and Adapt
Use analytics tools to track content performance.
Analyze data to understand what works and what doesn’t.
Adjust your strategy based on insights.
Example:
An e-commerce store monitors the conversion rate of product description pages.
If certain pages have lower conversions, they revise the content to better persuade shoppers.
8. Long-Term Focus
Content marketing is a marathon, not a sprint. Results may take time.
Stay committed to delivering quality content and building lasting relationships.
Example:
A competitive startup understands it may take months to gain substantial traction through content marketing.
They persistently create valuable content to establish authority.
9. Collaboration and Engagement
Encourage engagement by responding to comments, questions, and feedback.
Collaborate with influencers or partners to expand your reach.
Example:
An online fitness coach actively engages with followers on social media, responding to workout-related inquiries and collaborating with fitness influencers for joint content.
These core principles form the foundation of successful content marketing.
By applying these principles consistently, you can create content that attracts and engages your audience, builds lasting relationships, and drives business growth.
Top 21 Types of Content Marketing that You Should Know

Content marketing is a versatile strategy that thrives on diversity.
It offers numerous ways to connect with your audience, share valuable information, and achieve your business goals.
Content marketing comes in various formats, each serving a unique purpose in engaging and educating your audience.
Let’s dive deeper into these formats with detailed explanations and additional examples.
1. Blog Posts: Versatile Information Hubs
Blog posts are like digital articles that live on your website, making them accessible to your audience 24/7.
They are versatile and can cover many topics, making them a fundamental tool in your content marketing arsenal.
Types of Blog Posts:
- Educational Posts: These aim to teach your audience something new. For example, a gardening website can publish a post about “Growing Your First Tomato Plant.”
- How-To Guides: Step-by-step instructions on accomplishing a task, such as “How to Bake Perfect Chocolate Chip Cookies.”
- Listicles: Articles presented in a list format, like “10 Must-Have Travel Accessories for Your Next Trip.”
- Case Studies: Showcase real-life success stories of your customers using your product or service.
- Thought Leadership: Share your insights and opinions on industry trends or hot topics.
Example:
- A travel agency might write blog posts about travel destinations, packing tips, or travel stories to help and inspire their readers.
- A gardening supply store can create blogs about gardening techniques, plant care, or seasonal gardening advice.
2. Social Media Content: Heart of Online Interaction
Social media content is the lifeblood of online interaction, covering everything you post on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn.
It’s where conversations happen, and your audience engages with your brand.
Types of Social Media Content:
- Image Posts: Share striking visuals related to your brand or industry.
- Text Posts: Craft thought-provoking text-based content, like inspiring quotes or questions to spark discussions.
- Video Posts: Short videos that entertain, inform, or engage your audience.
- Live Streams: Real-time broadcasts to connect with your audience at the moment.
Example:
- A fashion brand can use Instagram to share photos of new arrivals, behind-the-scenes glimpses, and stories about their sustainability efforts.
- A local restaurant can post mouthwatering images of their daily specials on Instagram to attract diners.
- An animal shelter may share heartwarming adoption stories and pet care tips on Facebook to engage followers.
3. Video Content: Dynamic Engagement
Video content is a dynamic format that captures and sustains audience attention.
It can be used for various purposes, from showcasing products to telling your brand’s story.
Types of Video Content:
- Product Demonstrations: Show how your products work and their benefits.
- Interviews: Feature experts, team members, or customers to provide insights.
- How-To Guides: Step-by-step tutorials or guides on various topics.
- Behind-the-Scenes: Offer a sneak peek into your company’s inner workings.
Example:
- A cooking appliance manufacturer might create video content showing chefs using their products to prepare delicious recipes.
- An educational website could produce video tutorials explaining complex topics simply and visually.
- A fitness trainer might create workout videos to guide people through exercises and motivate them.
4. Infographics: Visual Simplicity
Infographics are visual representations of data or information.
They blend graphics and concise text to simplify complex concepts, making them easy to understand at a glance.
Types of Infographics:
- Statistical Infographics: Present data and statistics in a visually appealing manner.
- Process Infographics: Break down complex processes into step-by-step visuals.
- Comparison Infographics: Highlight differences or similarities between concepts.
- Timeline Infographics: Visualize historical events or project timelines.
Example:
- To raise awareness, a healthcare organization may design an infographic displaying key health statistics.
- An environmental organization can craft an infographic illustrating the impact of plastic pollution on marine life.
- A tech company might design an infographic showcasing the evolution of smartphones over the years.
5. Podcasts: Audio Insights
Podcasts are audio content people can listen to on platforms like Spotify and Apple.
They offer a unique way to share insights, stories, and discussions.
Types of Podcasts:
- Interview Podcasts: Host discussions with industry experts or thought leaders.
- Educational Podcasts: Share knowledge and insights on specific topics.
- Narrative Podcasts: Craft engaging stories to captivate your audience.
Example:
- A personal development coach might host a podcast series on goal setting featuring motivational interviews.
- A history enthusiast can host a podcast series delving into fascinating historical events, making history accessible to all.
- A cooking expert might share cooking tips, recipes, and food stories in a food-themed podcast.
6. Ebooks: In-Depth Information at Your Fingertips
Ebooks are digital books that provide extensive information on a specific topic.
They serve as valuable resources that readers can access conveniently on their devices.
Here’s a deeper dive into ebooks:
- Informative Guides: Ebooks often serve as informative guides, offering readers detailed insights into a subject. For instance, a software company might create an ebook explaining advanced programming techniques. This ebook can delve into complex coding concepts, providing developers with valuable knowledge.
- Lead Generation: Businesses frequently use ebooks as lead magnets. To access an ebook, readers typically provide their contact information, such as their email address. This exchange benefits both parties: Readers can access valuable content while businesses expand their email lists for future engagement.
- Versatile Topics: Ebooks can cover various topics, from technical guides and how-to manuals to industry trends and research findings. They allow brands to position themselves as experts in their field.
Example:
A marketing agency may offer an ebook, “A Comprehensive Guide to Social Media Advertising.”
This resource could comprehensively explore various platforms, ad formats, and optimization techniques, catering to marketers looking to enhance their social media advertising skills.
7. Whitepapers: In-Depth Analysis for Industry Insights
Whitepapers, like ebooks, offer detailed information but typically focus on industry-specific research, analysis, and problem-solving.
Let’s delve deeper into whitepapers:
- Industry Authority: Whitepapers establish a brand as an industry authority by presenting well-researched data and insights. They often address complex challenges and provide practical solutions.
- Research-driven: Whitepapers are research-driven documents relying on data, statistics, and expert opinions to support their claims. This makes them credible and informative resources.
- Audience Education: While whitepapers may require more technical language, they aim to educate and inform a specific audience. They’re commonly used in B2B (business-to-business) settings to address complex issues.
Example:
A cybersecurity company may release a whitepaper titled “Cyber Threats in the Modern Business Landscape.”
This document would analyze current cybersecurity trends, highlight emerging threats, and offer best practices for safeguarding business data.
8. Email Marketing: Building Relationships Through Email
Email marketing is a powerful tool for connecting with your audience directly.
It involves sending targeted emails to subscribers, offering a wide range of content and engagement opportunities:
- Newsletters: Regular email updates provide subscribers valuable content, company news, and insights. They maintain brand engagement and offer a personal touch.
- Product Updates: Product update emails inform customers about new features, improvements, or releases. They help retain existing customers by showcasing the value of your offerings.
- Promotions: Promotional emails offer discounts, exclusive offers, or limited-time deals to encourage purchases and engagement. They create a sense of urgency and excitement.
- Personalized Recommendations: Some businesses use data-driven personalized emails to recommend products or content based on individual preferences and behaviors.
Examples:
- An online bookstore can send a weekly newsletter featuring book recommendations, author interviews, and special discounts. This keeps readers informed about new releases and promotions while nurturing their interest in books.
- A software company might send an email announcing an update to their project management software, highlighting enhanced collaboration features and efficiency gains.
- An e-commerce fashion brand can send an email promoting a weekend sale with discounts on selected clothing items. This entices subscribers to shop and benefit from the limited-time offer.
- An online streaming platform may send personalized emails suggesting movies or TV shows similar to what a user has previously watched, enhancing user engagement.
9. Webinars: In-Depth Learning Experiences
Webinars offer a dynamic way to engage with your audience, providing in-depth knowledge and fostering interaction:
- Educational Platforms: Webinars serve as educational platforms where experts share insights, knowledge, and practical advice. They are often used to address complex topics.
- Real-Time Q&A: One of the key advantages of webinars is the ability to interact with the audience in real-time. Q&A sessions allow participants to ask questions and seek clarification.
- Broad Topic Range: Webinars can cover various topics, from industry trends and professional development to product demonstrations and tutorials.
Example:
A financial advisor may host webinars on retirement planning strategies.
These webinars could cover investment options, tax considerations, and wealth preservation, providing valuable guidance to participants.
10. Case Studies: Real-World Success Stories
Case studies are powerful tools for showcasing the real-world impact of your products or services:
- Detailed Analysis: Case studies provide in-depth analyses of your customers’ specific situations or challenges. They examine the problem, your solution, and the results achieved.
- Credibility Boost: By presenting successful outcomes, case studies build credibility and demonstrate your expertise. They offer tangible proof of your ability to deliver value.
- Customer-Centric: Case studies focus on the customer’s journey and experience, making them relatable and relevant to potential customers facing similar issues.
Example:
An IT company might share a case study illustrating how their cybersecurity solutions protected a client from a cyberattack.
This case study will outline the client’s security challenges, the solutions’ implementation, and the subsequent reduction in security incidents.
11. User-Generated Content: Audience Creativity
User-generated content involves encouraging your audience to become content creators, contributing to your brand’s storytelling:
- Customer Reviews: Encouraging customers to leave reviews on your website or third-party platforms provides authentic feedback and builds trust.
- Testimonials: Testimonials feature customers sharing their positive experiences with your products or services. They serve as powerful endorsements.
- Social Media Participation: Creating campaigns that encourage customers to share their experiences on social media with specific hashtags can generate valuable user-generated content.
Example:
A travel agency may run a contest where customers share their vacation photos on social media with a specific hashtag, such as #DreamVacationAdventures.
These photos become a part of the agency’s marketing material, showcasing real travelers’ experiences.
12. Interactive Content: Engaging and Educational
Interactive content is all about inviting your audience to actively participate.
It’s an effective way to educate, entertain, and gather valuable data.
Let’s delve into the world of interactive content and explore various engaging formats.
- Quizzes: Quizzes are a playful way to engage your audience while offering valuable insights. They can cover various topics, from personality assessments to product recommendations.
- Polls: Polls are excellent for gauging public opinion and encouraging interaction. They can ask questions, get feedback, or spark discussions.
- Interactive Infographics: Interactive infographics combine the power of visuals with user engagement. Users can click, hover, or scroll to reveal additional information.
- Calculators: Calculators provide practical value and range from financial planners to fitness trackers. Users input data, and the calculator generates personalized results.
- Visual Content: Visual content adds a splash of creativity to your marketing efforts. It encompasses images, GIFs, and memes, making it a powerful tool for boosting engagement and brand appeal.
- Images: Images are the backbone of visual content. They can include product photos, illustrations, and snapshots that tell a story.
- GIFs: GIFs bring a touch of animation to your content. They are short, looping clips that convey emotions, reactions, or brief demonstrations.
- Memes: Memes are humorous images or videos with clever captions. They tap into current trends and pop culture, making them highly shareable.
Examples:
- An eco-friendly brand might create a “Sustainability Quiz” to help users discover their environmental impact and provide improvement tips.
- A food delivery service may poll users to vote on their favorite new menu item.
- A tech company might create an interactive infographic showcasing the evolution of smartphones, allowing users to explore each model’s features.
- A mortgage lender can offer an “Affordability Calculator” to help users estimate their home-buying budget.
- An outdoor adventure brand can share breathtaking images of hikers conquering rugged trails.
- A fashion retailer can use GIFs to showcase the versatility of a new clothing collection through model movements.
- A coffee shop may create a meme about the struggle of waking up early, resonating with coffee lovers.
13. Long-Form Guides: In-Depth Knowledge
Long-form guides are comprehensive resources that offer in-depth insights into specific topics.
They position your brand as an industry authority and provide valuable information.
Long-form guides dive deep into a subject, covering it extensively.
They are often structured with chapters or sections for easy navigation.
Long-form guides often include expert opinions, tips, and real-world examples to give readers actionable advice.
Examples:
- A financial institution may create a guide on “Smart Investing Strategies” featuring insights from seasoned financial advisors.
- A health and wellness website can publish a “Complete Guide to Healthy Eating,” covering nutrition, meal planning, and recipes.
14. Newsletters: Ongoing Engagement
Newsletters are a consistent way to keep your audience informed and engaged.
They offer updates, insights, and exclusive content.
- Regular Updates: Newsletters are sent regularly, such as weekly or monthly. They can include news, articles, promotions, and event announcements.
- Exclusive Content: Newsletters often include exclusive content that subscribers won’t find elsewhere, encouraging them to stay subscribed.
Examples:
- An online bookstore sends a monthly newsletter with book recommendations, author spotlights, and upcoming book signings.
- A cooking website offers subscribers access to a monthly “Recipe of the Month” not available on the main site.
15. Social Media Stories: Timely and Engaging
Social media stories are short-lived, ephemeral content that can be used to share behind-the-scenes moments, product launches, or quick updates.
- Authentic Storytelling: Social media stories provide an authentic glimpse into your brand’s daily life. They are perfect for showcasing real moments and interactions.
- Product Teasers: Stories can build anticipation for product launches by sharing teasers, sneak peeks, and countdowns.
Example:
- An eco-conscious brand shares stories of their team participating in a beach cleanup event.
- A tech company creates stories revealing teaser images of an upcoming smartphone, gradually revealing its features.
16. Interactive Tools
Interactive tools are digital resources designed to engage users while providing practical value.
These tools often serve as problem solvers or sources of helpful information.
Example:
A health and fitness website might offer a “BMI Calculator.” Users input their height and weight, and the tool calculates their Body Mass Index, aiding them in assessing their fitness levels.
17. Live Streaming
Live streaming is akin to real-time TV on the internet.
Individuals or brands broadcast live video content that viewers can watch and interact with immediately through comments and questions.
Example:
A musician can conduct a live streaming session to perform their latest songs and connect with fans. Viewers can comment and request their favorite tunes during the show.
18. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Virtual Reality (VR) creates fully immersive digital environments, while Augmented Reality (AR) blends digital elements with the real world, enhancing the user’s experience.
Example:
A furniture store might offer an AR app that allows customers to visualize how a piece of furniture would look in their living room before making a purchase.
19. Micro-Moments Content
Micro-moment content focuses on delivering quick answers or solutions for specific, time-sensitive queries or needs. This content format aims to provide instant value.
Example:
A cooking website features a “15-Minute Recipes” section, offering fast and easy meal ideas for busy individuals seeking quick culinary solutions.
20. Interactive Emails
Interactive emails transform traditional email communication.
Recipients can engage directly in the email by clicking buttons, filling out forms, or purchasing.
Example:
An online bookstore sends an interactive email showcasing new arrivals. Readers can click on book covers to view details and make instant purchases without leaving their inbox.
21. Content Hubs
Content hubs function as organized repositories within a website, making it effortless for visitors to discover and explore a wide range of content.
Example:
An educational platform establishes a content hub named “Resource Center,” housing a collection of articles, videos, and downloadable materials for students seeking academic support.
These content marketing tactics offer a diverse toolkit for effectively engaging your audience.
Combining several strategies can help businesses connect with their target demographic across multiple channels and cater to various preferences and behaviors.
How Does Content Marketing Work?
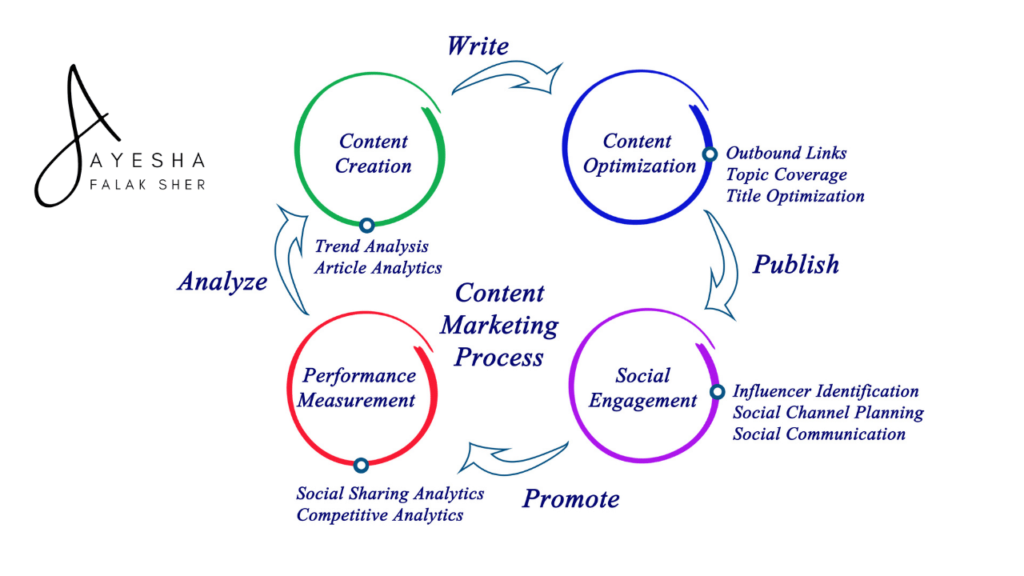
Content marketing is a strategic approach that involves creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and engage a specific target audience.
Its effectiveness lies in delivering the right content to the right people at the right time.
Here’s how it works:
1. Understanding Your Audience:
Content marketing begins with a deep understanding of your target audience.
You research their needs, preferences, pain points, and behaviors to create content that resonates with them.
2. Content Creation:
Once you know your audience, you create content tailored to their interests and challenges.
This content can take various forms, including blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, podcasts, and more.
3. Distribution:
Creating content is just the start.
To reach your audience effectively, you need to distribute it through the right channels.
This may include your website, social media, email newsletters, and industry publications.
4. Engagement:
Content should spark engagement and interaction.
Encourage comments, likes, shares, and discussions around your content.
Engagement helps build a community and strengthens relationships.
5. Providing Value:
Valuable content provides solutions, answers questions, or offers insights.
It positions your brand as a trusted resource and builds credibility.
6. Building Authority:
Consistently sharing expert insights and knowledge in your industry establishes your brand as an authority.
Thought leadership content helps in this regard.
7. Nurturing Leads:
Content can guide potential customers through the buying journey.
Consideration content, such as case studies and product comparisons, helps prospects make informed decisions.
8. Conversion:
Ultimately, content marketing aims to convert leads into customers.
Sales-focused content, like product descriptions and calls to action, plays a vital role here.
9. Measuring and Adjusting:
You measure key performance metrics to ensure your content marketing strategy is effective.
This data informs adjustments and refinements to your approach.
10. Long-Term Relationship:
Content marketing isn’t just about one-off interactions.
It aims to build long-term relationships with customers, fostering loyalty and advocacy.
So, content marketing operates as a bridge between your brand and your audience.
It’s about providing value, building trust, and guiding prospects from awareness to conversion.
Successful content marketing is a continuous process of understanding, creating, distributing, and refining content to meet the evolving needs of your audience.
Wrapping It Up:
So, there you have it—the essence of content marketing in simple terms.
It’s all about connecting with people.
First, you understand what prospects are looking for.
Then, you create something they like that helps or interests them.
Afterward, you share it where they hang out, like social media or emails.
People who see your helpful or interesting stuff might start liking your brand.
You build trust, like how you trust a friend’s advice.
Sometimes, this trust turns casual visitors into loyal customers.
And that’s the magic of content marketing—it’s not just words on a screen; it’s about building real connections.
So, as you dive into content marketing, remember it’s like chatting with friends.
Be helpful, be friendly, and watch those connections grow.
If you’re searching for an SEO content writer, YouTube script creator, or need help with copywriting, EBook writing, or SEO services, look no further.
Ayesha Falakk Sher is here to help you.
Connect with me today and take your content game to the next level.
Let’s craft engaging stories and build meaningful connections together.
Don’t hesitate—reach out now, and let’s get started on your content marketing adventure!